- >News
- >Ask CryptoVantage: Can You Use Bitcoin or Ethereum Without Internet?
Ask CryptoVantage: Can You Use Bitcoin or Ethereum Without Internet?
Like fish is to water, crypto is to the internet. That implies that cryptocurrencies rely on the internet to run. But as we know, internet connectivity is not always a given in a world where some governments have outright banned it, others have restricted it, some can reach for the kill switch depending on their mood, and it’s unreliable in other places.
Does that mean you should forget about using crypto like Bitcoin or Ethereum in such cases? Believe it or not, no. While it may sound counterintuitive, it’s possible to facilitate crypto transactions offline.
The only caveat is it would require preparation beforehand — buying specialized equipment, setting up, and more. So, while you can’t get up one random day and send crypto offline, it is technically possible with planning.
This piece explores several such scenarios and the technologies powering them. But first, a little background.
The Internet: Crypto's Backbone
Bitcoin and all cryptocurrencies rely on a technology called the blockchain — a sophisticated ledger able to be maintained by thousands of computers worldwide. These computers, or nodes in computing lingo, work together to maintain copies of the blockchain and verify transactions to prevent double-spending.
All these depend on one critical force: the internet. It’s thanks to the internet that:
- Nodes stay updated on transactions recorded on the blockchain
- Nodes are synced with the network
- Bitcoin can process transactions averaging about 300,000 daily.
- Individuals can “plug in” — that is, interact with crypto networks by sending and receiving crypto
In a perfect world, this buzz of activity would go on uninterrupted. However, that might not always be the case.
While the Bitcoin and Ethereum networks have managed to stave off debilitating security issues, the specter of threats like overzealous regulation hangs over them continuously.
How to Use Bitcoin Without The Internet
These realities have inspired creativity, with community members devising offline pathways for using Bitcoin and Ethereum. As of yet, most of the experimentation has been done on the king of crypto — no documented case exists for Ethereum yet. With that, here are a few ways to use Bitcoin without the internet:
#1. Satellite
The Blockstream Satellite is a product of a Canada-based Bitcoin technology company – Blockstream. They have ventured into the territory of making it possible to send bitcoin “offline”. The Blockstream Satellite is a network of six satellites positioned in space strategically to cover South America, North America, Africa, Europe, and Asia Pacific landmasses.
It’s stuff out of science fiction: these satellites are fed the Bitcoin network (read blocks) by ground stations dubbed “teleports.” The satellites then beam the Bitcoin network back to earth, allowing users to receive and verify Bitcoin transactions or broadcast their own transactions to the network without — an internet connection.
Anyone with basic satellite equipment like a low-cost satellite dish, can access and interact with the Blockstream Satellite. The downside is that it’s one way: while you can receive blockchain data via satellite, you can’t send transactions directly to the network. This means to send Bitcoin transactions, you still must rely on internet connectivity.
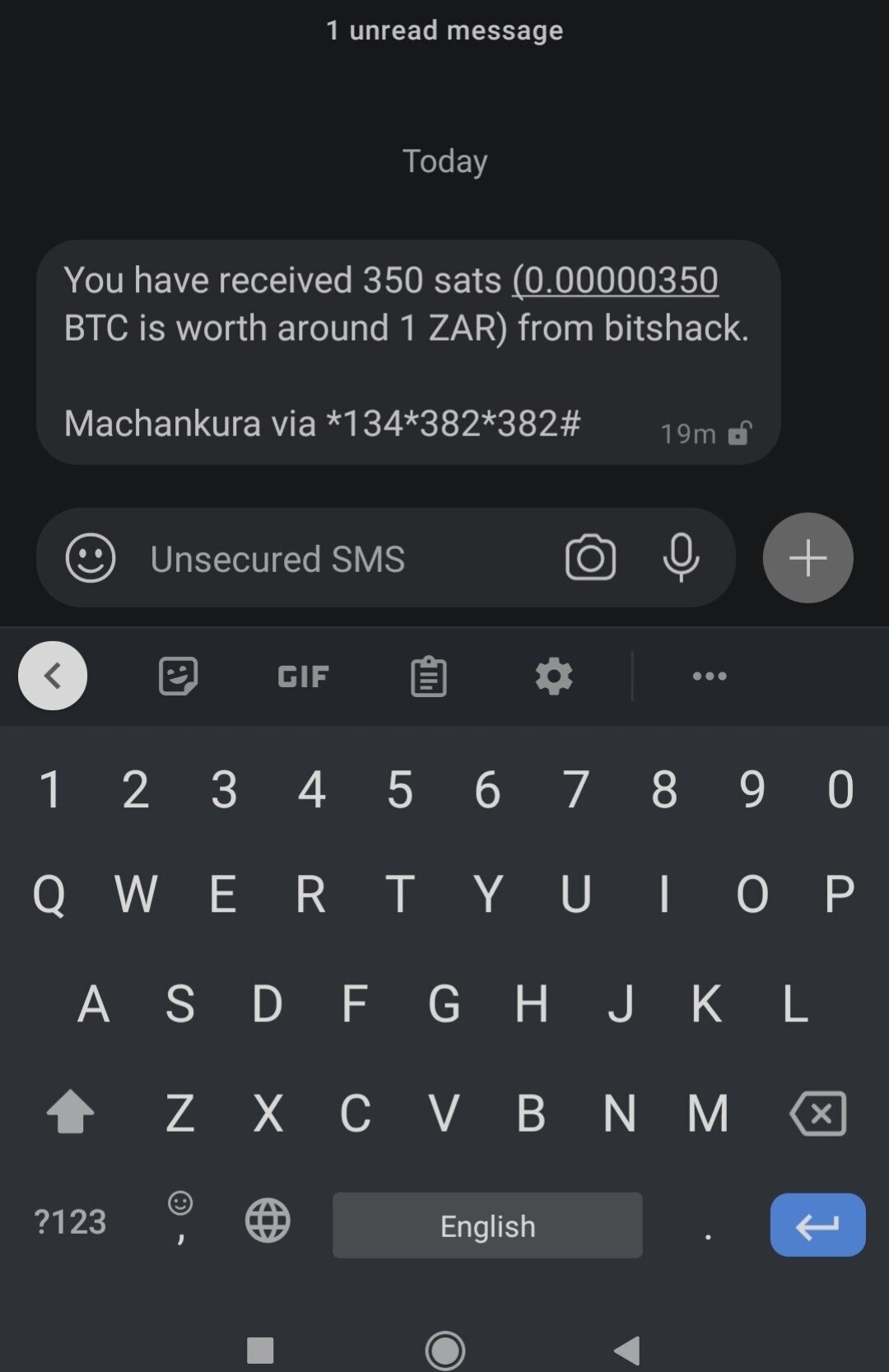
#2. Bitcoin by SMS
Citizens of eight African countries: Ghana, Kenya, Malawi, Namibia, Nigeria, South Africa, Uganda, and Zambia can send and receive Bitcoin even with a basic, old-school mobile phone. That’s thanks to a game-changing SMS-based innovation called Machankura.
Users only need to dial their country’s code to access the service, such as *483*8333# for Kenya or *347*8333# for Nigeria. You need mobile credit for the request to go through. You’ll then receive a menu with options for sending or receiving Bitcoin, viewing transaction history, and “bartering” your sats.
Source: Machankura’s Twitter page
By just dialing the code, Machankura creates a Bitcoin wallet for you. A Lightning Wallet address tied to your mobile number is also created.
Machankura, whose name is inspired by South African street lingo for “money” is a brainchild of developer Kgothatso Ngako.
#3. Amateur (Ham) Radio
Who knew you could send real crypto to the other side of the planet via radio waves? In 2019, this feat was accomplished between developers Rodolfo Novak and Bloomberg columnist, Elaine Ou.
Novak sent BTC from Toronto, Canada to Ou in San Francisco, California, over 2,600 miles. The duo used a set of off-the-shelf equipment for the transaction, including a 7.00 MHz antenna and a JS8Call.
The concept was first described by Nick Szabo, a renowned digital currencies pioneer, and Ou at the 2017 Bitcoin Scaling Conference.
#4. Mesh Networks
Mesh networks are a type of decentralized communication network where devices communicate with each other directly without the need for a centralized hub or server. Mesh networks were first proposed in the 70s for military communication but only became practical enough for commercial use in the 90s.
Due to its decentralized nature, this communication network lends itself well to crypto transactions. One such application leveraging them is TxTenna, a partnership between goTenna and Samourai Wallet that powers “off-grid transactions of signed Bitcoin transactions.” goTenna is a decentralized communications startup specializing in mesh technology.
In 2021, the companies teamed to launch TxTenna, an Android app that lets users send BTC without the internet. It allows users to connect their mobile phone with a goTenna device after activating the offline feature in the wallet app and using it to send Bitcoin.
The only downside is that the recipient must be within a one-mile radius and have an internet connection for the Bitcoin network to confirm the transaction.
Closing Thoughts: Difficult But Possible
It turns out that it’s possible to use Bitcoin or Ethereum without the internet. It’s not straightforward or perfect, but there are definitely options.
So far, amateur radio is the most perfect technique, allowing you to send and receive crypto without the internet, unlike satellite or mesh networks. For their part, SMS-based methods would work best only if cellular service is strong. Ultimately, it’s heartening to see these options embody the premise of Bitcoin as a catalyst for economic freedom.